
When you create a virtual disk for a guest operating system, select Allocate all disk space now.
For ESXi hosts, create virtual disks as preallocated. If the combined disk I/O is higher than a single HBA capacity, use multipathing or multiple links. On systems with sizable RAM, disable memory trimming by adding the line MemTrimRate=0 to the virtual machine's VMX file. This alleviates disk spindle contention during periods of high use. For resource-intensive virtual machines, separate the virtual machine's physical disk drive from the drive with the system page file. If not, increase the number of outstanding disk requests for the virtual machine by adjusting the Disk.SchedNumReqOutstanding parameter. Verify that the queue depths and cache settings on the RAID controllers are adequate. Configure the HBAs and RAID controllers for optimal use. Use separate queues for each adapter to improve disk efficiency. Spread heavily used storage across LUNs that are accessed by different adapters.  Balance the disk load across all physical resources available. Use Storage vMotion to distribute I/O-intensive virtual machines across multiple hosts.
Balance the disk load across all physical resources available. Use Storage vMotion to distribute I/O-intensive virtual machines across multiple hosts. 
Consider array-side improvements to increase throughput. When too many servers simultaneously access common elements on an array, the disks might have trouble keeping up. Use the vendor's array tools to determine the array performance statistics.If appropriate for your environment, disable antivirus on-demand scans on the VMDK and VMEM files.Defragment the file systems on all guests.Install VMware Tools so that memory ballooning can occur. Increase the guest memory, but not to an extent that leads to excessive host memory swapping. Check swap statistics in the guest operating system to verify that virtual machines have adequate memory.Increasing memory might reduce the need to store data because some workloads can utilize system memory to cache data and avoid disk access. Note: It may require you to increase the host memory.
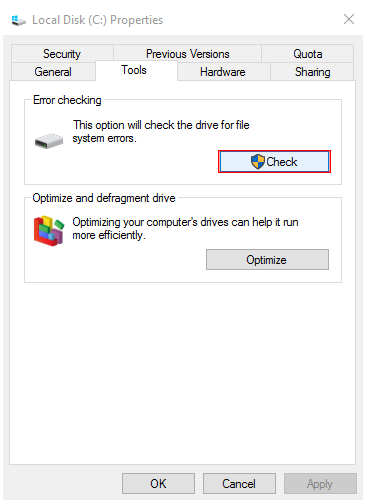
Doing so should allow for more operating system caching, which can reduce I/O activity.
Move the active VMDK to a volume with more spindles or add disks to the LUN. Check the CPU usage, and increase the queue depth. The virtual machines on the host are trying to send more throughput to the storage system than the configuration supports.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
